Why does my internet keep going out? 12 Common Causes & Easy Fixes

Introduction
Few things are more frustrating than your WiFi cutting out right in the middle of a video call, streaming session, or online game. If you’ve ever wondered why does my internet keep going out, you’re not alone.
This problem can stem from multiple sources your devices, router, Internet Service Provider (ISP), signal interference, or even outdated hardware.
In this detailed guide, we’ll walk through 12 common reasons your WiFi keeps disconnecting and exactly how to fix each one. We’ll also include a quick-reference table for easy troubleshooting.
At-a-Glance: Common Problems vs Fixes
| Problem | Quick Fix |
| Too many devices | Disconnect unused gadgets, enable QoS |
| Poor router placement | Move router to a central, elevated spot |
| Radio interference | Switch to 5GHz/6GHz band |
| Overheating router | Reboot and keep ventilated |
| Outdated drivers | Update or replace network card |
| Wrong WiFi band | Use 5GHz for high-speed devices |
| Damaged cables | Replace with Cat6 or better |
| ISP outage | Contact provider or check outage map |
| Dust buildup | Clean router vents and ensure airflow |
| System corruption | Reset network settings and run scans |
| Weak security | Update passwords and disable WPS |
| Old equipment | Upgrade to WiFi 6 or mesh system |
1. Too Many Devices Are Connected
Why It Happens
When multiple devices — phones, smart TVs, cameras, laptops, and IoT gadgets — connect simultaneously, they compete for the same bandwidth. Even a high-speed plan can choke when overloaded, leading to periodic dropouts.
How to Fix
- Disconnect unused or idle devices.
- Limit background tasks such as cloud backups or auto-updates.
- Upgrade to a router with higher bandwidth capacity or a tri-band model.
- Enable Quality of Service (QoS) in your router settings to prioritize critical devices (like work laptops).
2. The Router Is in a Poor Location
Why It Matters
WiFi signals weaken when your router is tucked away behind walls or placed near metal objects. Microwaves, cordless phones, and even fish tanks can disrupt the signal.
How to Fix
- Place your router in a central, elevated position — ideally above furniture and away from corners.
- Avoid placing it near walls, appliances, or heavy metal objects.
- For large spaces, invest in WiFi range extenders or a mesh WiFi system to eliminate dead zones.
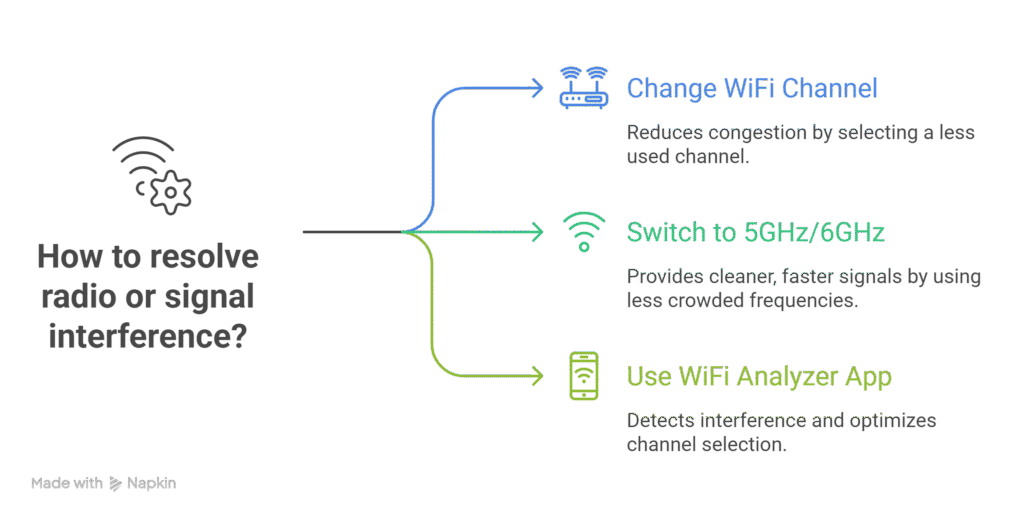
3. Radio or Signal Interference
Why It Happens
Nearby WiFi networks, Bluetooth devices, and even baby monitors share the same 2.4GHz frequency, creating overlapping signals that cause instability.
How to Fix
- Log in to your router settings and change the WiFi channel to one with less congestion.
- If available, switch devices to 5GHz or 6GHz for cleaner, faster signals.
- Use a WiFi analyzer app (like NetSpot or WiFi Analyzer) to detect interference and optimize channel selection.
4. Your Router Needs a Break (Overheating or Software Lag)
Why It Happens
Just like computers, routers can overheat or develop software glitches over time. Long uptime can cause memory leaks or sluggish performance, resulting in disconnections.
How to Fix
- Turn off your router and modem for about 10 minutes, then restart them.
- Schedule automatic weekly reboots via the router interface.
- Keep the router in a well-ventilated area.
- Regularly update firmware from the manufacturer’s site to fix known bugs and enhance stability.
5. Outdated or Faulty Wireless Card / Drivers
Why It Happens
Old or corrupted network drivers often cause devices to drop WiFi intermittently. This is especially common after major OS updates.
How to Fix
- Update drivers through Windows Update or the manufacturer’s website.
- If your device still disconnects, replace the wireless card (common in older laptops).
On Windows, reset network settings by typing:
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset
ipconfig /flushdns
- Reboot your computer after running these commands.
6. Using the Wrong WiFi Band (2.4GHz vs 5GHz)
Why It Happens
Most routers broadcast on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. The 2.4GHz band covers longer distances but is slower and more congested. 5GHz offers faster speeds but shorter range.
How to Fix
- Connect bandwidth-heavy devices (like PCs and TVs) to 5GHz.
- Use 2.4GHz for smart devices that don’t require high speed.
- Enable band steering if your router supports it, allowing devices to switch automatically to the optimal band.
7. Faulty or Damaged Cables
Why It Happens
A damaged Ethernet, coaxial, or power cable can break your connection intermittently. Even slight fraying or loose connectors can cause frequent drops.
How to Fix
- Inspect cables for physical wear, bends, or kinks.
- Replace old cables with Cat6 or Cat7 for stronger, faster performance.
- Use surge protectors to prevent electrical spikes that can harm your modem or router.
8. Service Provider (ISP) Outages or Line Issues
Why It Happens
Sometimes, the issue isn’t in your home at all. ISPs perform maintenance, or external line faults can cause temporary downtime.
How to Fix
- Check your ISP’s outage map or customer portal for service alerts.
- Test your connection using a mobile hotspot to confirm if the issue is external.
- Contact customer support for diagnostics or a line inspection if the problem recurs frequently.
9. Dust and Overheating in Equipment
Why It Happens
Dust can clog router vents, trapping heat and throttling performance. Excessive heat leads to automatic restarts or dropped signals.
How to Fix
- Use compressed air to clean vents and ports monthly.
- Keep routers off carpets or enclosed cabinets.
- Maintain ambient airflow to avoid overheating.
10. Corrupted PC or Device Files
Why It Happens
Operating system errors, malware, or corrupted network stacks can interfere with your WiFi connection.
How to Fix
- Use the Windows Network Troubleshooter (Settings → Network & Internet → Troubleshoot).
- Reset TCP/IP and DNS configurations via Command Prompt.
- Scan your device for malware or system integrity errors.
- On macOS, renew the DHCP lease in network settings to refresh IP allocation.
11. Weak WiFi Security or Unauthorized Access
Why It Happens
If your WiFi is unsecured or uses outdated encryption (like WEP), others might piggyback on your network, draining bandwidth and causing instability.
How to Fix
- Update your network to WPA2 or WPA3 encryption.
- Use a strong, unique password.
- Disable WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) and unnecessary guest networks.
- Regularly check the list of connected devices in your router dashboard.
12. You Might Need New Equipment
When It’s Time to Upgrade
If your router or modem is more than five years old, it may not support modern WiFi standards. Frequent disconnects, even after troubleshooting, usually signal hardware fatigue.
Recommended Fix
- Upgrade to a WiFi 6 or WiFi 6E router for improved range, speed, and device management.
- Ensure your modem supports your ISP’s latest DOCSIS standard.
- For multi-floor homes, a mesh WiFi system offers seamless coverage and fewer drops.
Advanced Fixes (For Tech-Savvy Users)
If you’ve tried everything above and still find your WiFi dropping:
- Adjust MTU size and channel width in router settings for optimal performance.
- Assign static IPs to critical devices (like gaming consoles or workstations).
- Change your DNS servers to Google (8.8.8.8 / 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) for faster, more stable resolution.
- Use a UPS backup to prevent disconnections during brief power outages.
Preventive Tips to Keep WiFi Stable Long-Term
- Reboot your router at least once a week.
- Keep firmware and drivers up to date.
- Clean hardware periodically to prevent overheating.
- Limit background syncing (cloud, gaming updates, etc.).
- Run regular speed tests to monitor ISP performance.
FAQs: Why Does My WiFi Keep Disconnecting?
1. Why does my WiFi disconnect only on one device?
It’s likely a driver issue or corrupted network profile. Update drivers or reset network settings on that device.
2. Why does it cut out at the same time every day?
Scheduled router reboots or ISP maintenance can cause this. Check router logs or contact your provider.
3. How do I fix my router dropping connection every few minutes?
Reboot, update firmware, and ensure your router isn’t overheating or overloaded.
4. Why does my phone keep losing WiFi signal?
Try forgetting and reconnecting to the network. Update your phone’s OS, or switch to a less congested band.
5. How can I improve WiFi connection in rural areas?
Use a high-gain external antenna or LTE/5G WiFi solution. Consider Starlink or other satellite ISPs for reliable access.
6. When should I replace my router or modem?
Every 4–5 years, or sooner if it no longer supports your ISP’s speed tier or latest protocols.
Conclusion
If you’ve been asking why does my internet keep going out, the problem often isn’t one big failure it’s a mix of small issues like signal interference, outdated firmware, or hardware fatigue.
Start with the simplest fixes: move your router, disconnect idle devices, and reboot your hardware. If disconnections persist, consider upgrading to a WiFi 6 router or contacting your ISP for a line check.
Reliable WiFi isn’t just a convenience — it’s a necessity for streaming, gaming, and remote work. Stabilize your connection today and enjoy uninterrupted online experiences.